Climbing robots might have many helpful real-world purposes, starting from the completion of upkeep duties on roofs or different tall buildings to the supply of parcels or survival kits in places which can be tough to entry. To be efficiently deployed in real-world settings, nonetheless, these robots ought to be capable to successfully sense and map their environment, whereas additionally precisely predicting the place they’re situated inside mapped environments.
Researchers at Guangdong College of Expertise lately developed a brand new technique to reinforce the flexibility of a bipedal climbing robotic to estimate its state and map its environment whereas climbing a truss (i.e., a triangular system consisting of straight interconnected components, which could possibly be a bridge, roof or one other man-built construction). Their proposed technique, launched in Robotics and Autonomous Methods, is predicated on a simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) algorithm.
“Our latest work deploys SLAM strategies to a specific biped climbing robotic (BiCR), which was developed by our lab, named the Biomimetic and Clever Robotics Lab,” Weinan Chen, co-author of the paper, instructed Tech Xplore.
“BiCR is an electromechanical system much like a transferring manipulator that is ready to transfer through grippers at each ends and rotate with a number of joints. The robotic can be utilized for set up, upkeep, and inspection in high-altitude and high-risk environments, reminiscent of development web site scaffolding and energy towers.”
The first goal of the latest examine by Chen and his colleagues was to permit a bipedal climbing robotic to autonomously localize itself and create a map of environment whereas navigating environments characterised by truss buildings. The SLAM-based strategy they suggest was particularly utilized to BiCR, a bipedal climbing robotic beforehand developed at their lab.
“Since there are lots of variations within the configurations and dealing environments of the BiCR and different robots (floor automobiles, UAVs, and so forth.), this paper proposes a technique that fuses robotic joint data and environmental data to enhance the localization accuracy of the BiCR,” Chen mentioned.
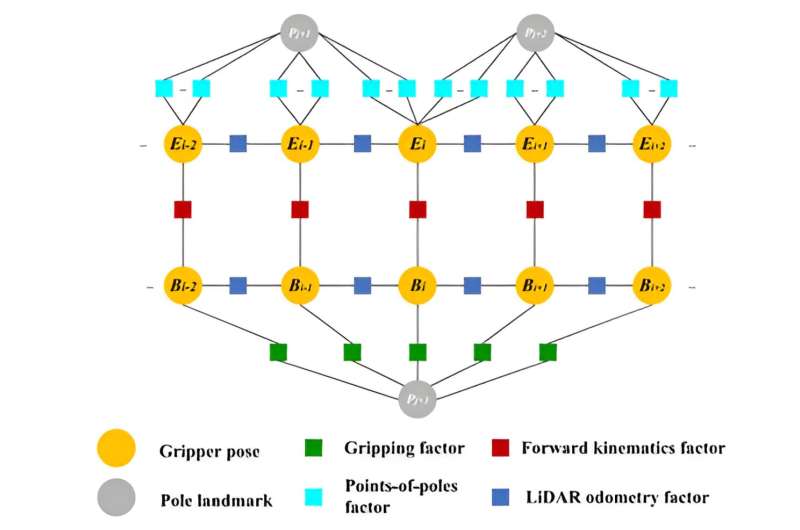
BiCR-SLAM, the simultaneous localization and mapping system developed by the researchers, makes use of details about the BiCR robotic’s configuration, a LiDAR sensing system and visible knowledge collected by cameras to localize a robotic and map the truss it’s climbing. The framework can decide the pose of the robotic gripper and create a map of poles surrounding the gripper, in order that it may possibly higher plan its actions whereas climbing a truss.
“The framework consists of 4 elements: an encoder lifeless reckoning, a LiDAR odometry estimation instrument, a pole landmark mapping mannequin, and a world optimization approach,” Jianhong Xu, one other creator of the paper, mentioned. “Within the international optimization, we suggest a multi-source fusion issue graph to collectively optimize the robotic localization and pole landmarks.”
A notable benefit of BiCR-SLAM is that it concurrently considers data associated to the bipedal robotic’s joints and knowledge collected by sensors. It thus permits the BiCR robotic to map its environment and predict its pose, utilizing this data to plan its subsequent strikes and safely climb a truss.
“The system may also hold working in some low-texture and single-structure truss environments,” Chen mentioned. “To the perfect of our data, BiCR-SLAM is the primary SLAM system resolution to include BiCR’s data for a truss map. This work can advance the event of BiCR and SLAM and enhance BiCR’s localization and navigation efficiency in autonomous operations.”
Whereas Chen and his collaborators particularly designed their SLAM technique for the BiCR robotic, sooner or later it is also tailored and utilized to different climbing robots. To this point, the group used a single LiDAR system to sense poles inside a small sensing vary round a robotic, however they quickly hope to additional advance its capabilities utilizing extra of those methods together with deep studying strategies.
“In our subsequent research, we plan to make use of a number of LiDARs to sense pole objects utilizing deep studying approaches which can be free from the calibration of the exterior parameters between numerous sensors,” Chen added.
“We additionally plan to make use of the sensing configuration with a extra in depth scanning vary to enhance segmentation accuracy and apply this work to the autonomous navigation of climbing robots. Particularly, we’ll combine the movement planning half to appreciate an autonomous navigation operate.”
© 2024 Science X Community

