The most recent wearable units, corresponding to Samsung’s Galaxy Ring and Apple’s Imaginative and prescient Professional, are taking well being care a step additional and even enabling individuals to work just about. Given the traits of wearable units that require them to be small and light-weight, there’s an inevitable limitation on battery capability, nonetheless presenting a technical barrier to incorporating a wide range of features. To ensure that wearable units to completely notice their potential, it’s essential to develop a lighter and ‘extra from much less’ vitality storage methodology.
A joint analysis workforce led by Dr. Hyeonsu Jeong and Namdong Kim of the Middle for Useful Composite Supplies, Jeonbuk Department, and Dr. Seungmin Kim of the Middle for Carbon Fusion Supplies has developed a fiber-like electrode materials that may retailer vitality. The analysis is printed within the journal Superior Vitality Supplies.
The fibers are robust, light-weight, and extremely versatile, enabling better freedom in wearable system type elements and the flexibility to be made into varied shapes and functions.
Carbon nanotube fibers are versatile, light-weight, and possess wonderful mechanical and electrical properties, making them a promising materials for wearable units. Nevertheless, as a result of their small particular floor space and lack of electrochemical exercise, earlier research have primarily used them as a present collector and coated their floor with lively supplies.
Nevertheless, this method just isn’t solely uneconomical because of the excessive price of further supplies and processes, but in addition has a excessive likelihood of separation of the lively materials from the fiber throughout long-term use or bodily deformation.
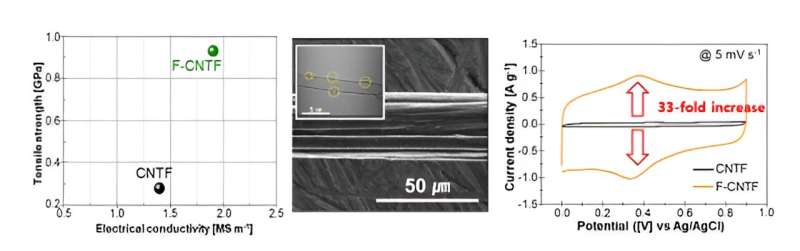
To unravel this downside, the Korea Institute of Science and Know-how (KIST) analysis workforce developed a fibrous electrode materials with excessive vitality storage capability with out the necessity for lively supplies. The workforce developed carbon nanotube fibers with each electrochemical exercise and wonderful bodily properties by acid-treating and modifying powder-form carbon nanotubes, adopted by spinning them into fibers.
The modified carbon nanotube fiber has 33 occasions extra vitality storage capability, 3.3 occasions extra mechanical power, and greater than 1.3 occasions extra electrical conductivity than strange carbon nanotube fibers. Furthermore, for the reason that vitality storage electrode materials was developed utilizing solely pure carbon nanotube fibers, it may be mass-produced utilizing moist spinning expertise.
When examined with fiber-shaped supercapacitors, they retained practically 100% of their efficiency when knotted and 95% of their efficiency after 5,000 bending exams. In addition they carried out nicely when woven into the wrist straps of digital watches utilizing a mix of standard and carbon nanotube fibers, after being bent, folded, and washed.
Dr. Kim Seung-min of KIST stated, “We have now confirmed that carbon nanotubes, which have just lately began to draw consideration once more as a conductive materials for secondary batteries, can be utilized in a a lot wider vary of fields.”
“Carbon nanotube fiber is a aggressive area as a result of we now have the unique expertise and there’s not a lot of a expertise hole with superior international locations,” stated Dr. Hyeon Su Jeong, a co-researcher, including, “We are going to proceed our analysis to use it as a core materials for atypical vitality storage.”
One other co-researcher, Dr. Nam-dong Kim, stated, ” We’re presently conducting analysis to use this expertise to fiber-type batteries with increased vitality density, going past supercapacitors. .”

